Add a New Account
Adding a new account is simple. Follow these instructions.
1. Click Account / Add New.
2. The screen is blank. The system will assign the next account number. You may change that number if you want. It must be unique. Fill in all the other information such as addresses, numbers, email, etc.
3. When all the generic account information is entered, click Next, Previous then Save. Then continue on to “Add A New Service.”
Note: Step 3 is very important. When creating a new account the index on the tables are temporary. If Next, Previous and then Save are not clicked the index will not become permanent and when the account is accessed the account will be gone.
Note: The PIDN may be changed at this time only. If the PIDN is changed after services and charges are added the links between the tables will be changed and the data will become orphaned and inaccessible.
Capsoft.us is a global software development firm offering government collection applications in network, online and mobile apps.
Wednesday, December 30, 2009
Defining a Billing File within CSI Utility Billing and Revenue Management Software.
What is a billing file (BF?)
To group all of the accounts for readings, Capital creates a billing file (BF) each month. Billing File is a generic name assigned to the accounts you are about to read. Each time you CLICK the CREATE BILLING FILE button; the system goes to the service tab and gathers all of the accounts that qualify. The system then puts them into a billing file and adds a number to the end of it like BF100. You can create as many billing files, as you want. The purpose of the billing file is to give you a clean reading entry system and history of all the readings you’ve done in the past. Billing files hold all the services, dates, readings and usage information for a given DUE DATE.
To group all of the accounts for readings, Capital creates a billing file (BF) each month. Billing File is a generic name assigned to the accounts you are about to read. Each time you CLICK the CREATE BILLING FILE button; the system goes to the service tab and gathers all of the accounts that qualify. The system then puts them into a billing file and adds a number to the end of it like BF100. You can create as many billing files, as you want. The purpose of the billing file is to give you a clean reading entry system and history of all the readings you’ve done in the past. Billing files hold all the services, dates, readings and usage information for a given DUE DATE.
Tuesday, December 29, 2009
How to Setup a Billing Grid within CSI Utility Billing and Revenue Management Software.
1. Apply a cycle name such as Month.
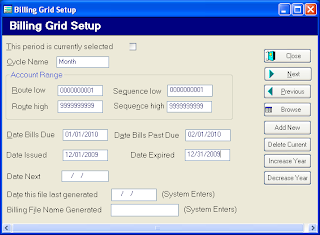
2. Account Range should be as follows (to include all your accounts):
RL – 0000000001 RH – 9999999999
SL – 0000000001 SH – 9999999999
3. Bills Due – Enter the Due Date
4. Past Due – Enter the Date you want Penalties Applied. You must enter a Past Due Date.
5. Date Next Reading is the next time you want to apply this charge to the accounts. This is optional
6. You can define as many cycles as desired. Cycles only need to be setup one time. Next year when you want to update the year for each of your cycles, CLICK the INCREASE YEAR BUTTON. That will save time.
Note: If you are unsure as to which grid to increase year, or are finding that the billing file is not pulling the correct date, we suggest creating new grids each year to alleviate any confusion (i.e. not using the increase year button.)
Note: Defining cycles require thought and most of which is completed during training.
After all the CYCLES are defined you are ready to gather readings and bill.
Note: The cycle name entered must be exactly the same as the cycle on the services entered. When a computer searches it is looking for exact matches. (Month, month or Monthly is not the same to a computer. The difference in upper and lower case M’s and suffix makes these cycles different.)

2. Account Range should be as follows (to include all your accounts):
RL – 0000000001 RH – 9999999999
SL – 0000000001 SH – 9999999999
3. Bills Due – Enter the Due Date
4. Past Due – Enter the Date you want Penalties Applied. You must enter a Past Due Date.
5. Date Next Reading is the next time you want to apply this charge to the accounts. This is optional
6. You can define as many cycles as desired. Cycles only need to be setup one time. Next year when you want to update the year for each of your cycles, CLICK the INCREASE YEAR BUTTON. That will save time.
Note: If you are unsure as to which grid to increase year, or are finding that the billing file is not pulling the correct date, we suggest creating new grids each year to alleviate any confusion (i.e. not using the increase year button.)
Note: Defining cycles require thought and most of which is completed during training.
After all the CYCLES are defined you are ready to gather readings and bill.
Note: The cycle name entered must be exactly the same as the cycle on the services entered. When a computer searches it is looking for exact matches. (Month, month or Monthly is not the same to a computer. The difference in upper and lower case M’s and suffix makes these cycles different.)
Creating Billing Grid for CSI Utility Billing Software
Apply a cycle name such as Month.
Account Range should be as follows (to include all your accounts):
RL – 0000000001 RH – 9999999999
SL – 0000000001 SH – 9999999999
Bills Due – Enter the Due Date
Past Due – Enter the Date you want Penalties Applied. You must enter a Past Due Date.
Date Next Reading is the next time you want to apply this charge to the accounts. This is optional
You can define as many cycles as desired. Cycles only need to be setup one time. Next year when you want to update the year for each of your cycles, CLICK the INCREASE YEAR BUTTON. That will save time.
Note: If you are unsure as to which grid to increase year, or are finding that the billing file is not pulling the correct date, we suggest creating new grids each year to alleviate any confusion (i.e. not using the increase year button.)
Note: Defining cycles require thought and most of which is completed during training.
After all the CYCLES are defined you are ready to gather readings and bill.
Note: The cycle name entered must be exactly the same as the cycle on the services entered. When a computer searches it is looking for exact matches. (Month, month or Monthly is not the same to a computer. The difference in upper and lower case M’s and suffix makes these cycles different.)
Account Range should be as follows (to include all your accounts):
RL – 0000000001 RH – 9999999999
SL – 0000000001 SH – 9999999999
Bills Due – Enter the Due Date
Past Due – Enter the Date you want Penalties Applied. You must enter a Past Due Date.
Date Next Reading is the next time you want to apply this charge to the accounts. This is optional
You can define as many cycles as desired. Cycles only need to be setup one time. Next year when you want to update the year for each of your cycles, CLICK the INCREASE YEAR BUTTON. That will save time.
Note: If you are unsure as to which grid to increase year, or are finding that the billing file is not pulling the correct date, we suggest creating new grids each year to alleviate any confusion (i.e. not using the increase year button.)
Note: Defining cycles require thought and most of which is completed during training.
After all the CYCLES are defined you are ready to gather readings and bill.
Note: The cycle name entered must be exactly the same as the cycle on the services entered. When a computer searches it is looking for exact matches. (Month, month or Monthly is not the same to a computer. The difference in upper and lower case M’s and suffix makes these cycles different.)
What is required for a service to qualify for a reading in the Utility Billing Software.
Qualify to get a Reading
To create a reading / billing file the system looks at 3 main fields in the Service to decide whether to include it or not.
1. Status. The Account level status must be Active and the Service level status must be Active or Suspend
2. The Route and Sequence must be entered so the system can put the reading file in the correct walking order.
3. Cycle. The Cycle must match on all the accounts you are trying to pull out into your reading file. The cycle on each level must be spelled exactly the same, Month and month are not the same to a computer.
To create a reading / billing file the system looks at 3 main fields in the Service to decide whether to include it or not.
1. Status. The Account level status must be Active and the Service level status must be Active or Suspend
2. The Route and Sequence must be entered so the system can put the reading file in the correct walking order.
3. Cycle. The Cycle must match on all the accounts you are trying to pull out into your reading file. The cycle on each level must be spelled exactly the same, Month and month are not the same to a computer.
Reasons for Automatic Status Changes within the Utility Billing Software.
Automatic Status Changes
There are a few situations where the system will automatically change the status of your services and account from ACTIVE. The factors that need to have attention paid to them are on the service level and need to be corrected before the billing file is created
1. If, on the service detail screen, the date Final field value is less than the Period Start date, upon generation of the billing file, the property status will change to CLOSE.
2. If, the property alert 3 or Move In value is greater than the period end date then the status will change to HOLD.
3. If, the property alert 3 or Move In value is in between the period start and end dates the status will change to ACTIVE.
Note: The Move In Update Services Button (above right image, Just below the Apply Deposit button), when pushed will change the status to Active and clear the Date Final Field.
There are a few situations where the system will automatically change the status of your services and account from ACTIVE. The factors that need to have attention paid to them are on the service level and need to be corrected before the billing file is created
1. If, on the service detail screen, the date Final field value is less than the Period Start date, upon generation of the billing file, the property status will change to CLOSE.
2. If, the property alert 3 or Move In value is greater than the period end date then the status will change to HOLD.
3. If, the property alert 3 or Move In value is in between the period start and end dates the status will change to ACTIVE.
Note: The Move In Update Services Button (above right image, Just below the Apply Deposit button), when pushed will change the status to Active and clear the Date Final Field.
Billing vs. Printing within Capital Software Utility Billing.
Applying Charges and Printing are two totally separate topics in the Utility Bill System. The act of applying charges can be performed at any time through a manual or automated procedure.
The billing statements that come standard with The Utility Bill system perform a real-time refresh of the outstanding charges prior to printing the statements. For example, if you are preparing to print your bills and you notice something is incorrect on a single account, you would go to the Charges tab on that account, fix the problem and redo the billing wizard to generate your bills.dbf source file for printing. It would instantly reflect the change.
REMEMBER TO ALWAYS RUN A MANUAL RECALCULATION PRIOR TO RUNNING THE BILLING WIZARD TO ENSURE YOUR ACCOUNTS’ CHARGES ARE CURRENT.
The billing statements that come standard with The Utility Bill system perform a real-time refresh of the outstanding charges prior to printing the statements. For example, if you are preparing to print your bills and you notice something is incorrect on a single account, you would go to the Charges tab on that account, fix the problem and redo the billing wizard to generate your bills.dbf source file for printing. It would instantly reflect the change.
REMEMBER TO ALWAYS RUN A MANUAL RECALCULATION PRIOR TO RUNNING THE BILLING WIZARD TO ENSURE YOUR ACCOUNTS’ CHARGES ARE CURRENT.
What is the Borland Database Engine or BDE.
The Boreland Database Engine is like a middle man between the software you see on your screen and the location of the physical data. The BDE manages the flow of data back and forth between the screen you see and the database. The BDE must be pointing to the correct location of the data or the program will not function. The connection is established at the time of logging into the program. In The Utility Bill, the BDE path is displayed at the top of the program. The default location is c:\capsoft\util32.
What to do if penalties do not show up on the accounts and they are late today?
You may consider one of 2 solutions. First, check the charges tab of an account you know is late. Display a late line item. Is there a PAST DUE date entered? That is the main trigger the system uses. If there is a date, then the second option is to run the Manual Recalculation. This program controls all calculations within the software. If neither of these options works, contact Technical Support at 888-553-9991 extention 1 or on our website at www.capitalsoftwareinc.com.
How to backdate a payment to remove a penalty from Capital Software Utility, Property Tax and Revenue Management Applications.
How do I backdate a payment to remove a penalty?
1. Right CLICK in the EFFECTIVE DATE BOX on the front , or property screen, and select the true payment date.
2. After selecting the system will pretend it is that day.
3. CLICK the Take a Payment Button.
4. Enter check number and CLICK OK
1. Right CLICK in the EFFECTIVE DATE BOX on the front , or property screen, and select the true payment date.
2. After selecting the system will pretend it is that day.
3. CLICK the Take a Payment Button.
4. Enter check number and CLICK OK
What is the difference between the Date Due and the Date Past Due within Capital Software Applications.
Both of those dates have jobs that they perform. One is to be used for when the charges go into affect and the other is used for delinquents. I bet you can guess which one does which. The date due is the main date inside of the system. All of the billing reports are based on the date due. It is the one thing that will always be consistent on each charge.
The system starts counting the number of elapsed days from that date and does not stop until it is paid. Once it is paid the system stops counting the elapsed days and the charges are considered finished. In the trancode setup for penalty and interest you may have seen a field called days. Once the charge has reached that number of elapsed days then it looks at the next item we will discuss which is the date past due.
The date past due is really the last straw before the penalty and interest start applying. Once the computer passes the date past due, it then looks at the days setup in the Tran Code to see if the elapsed days has also past. When the elapsed days have passed and the date past due has passed, then the account is bound to get penalty and interest applied to it. If an account is missing a date past due, it will never get a spawned penalty or interest charge because a date that looks like this ( / / ) will never become delinquent.
The system starts counting the number of elapsed days from that date and does not stop until it is paid. Once it is paid the system stops counting the elapsed days and the charges are considered finished. In the trancode setup for penalty and interest you may have seen a field called days. Once the charge has reached that number of elapsed days then it looks at the next item we will discuss which is the date past due.
The date past due is really the last straw before the penalty and interest start applying. Once the computer passes the date past due, it then looks at the days setup in the Tran Code to see if the elapsed days has also past. When the elapsed days have passed and the date past due has passed, then the account is bound to get penalty and interest applied to it. If an account is missing a date past due, it will never get a spawned penalty or interest charge because a date that looks like this ( / / ) will never become delinquent.
How Does an account within Captial Software Property Tax Software become Delinquent?
The Tax Bill™ performs all calculations in a program called recalculation.exe. This program looks at every charge on every account. While evaluating a charge, if it has a gross balance greater than zero, the system will look at the Date Past to see if it is delinquent. If the system date of the computer is greater than the Date Past then the account becomes delinquent.
The Delinquent field on the Account screen will have the calculated delinquent amount. The delinquent charges will have the status of Past Due. The system will also spawn any penalty and interest charges at this time if setup to do so.
Note – The Date Past Due must have a date present to be considered for past due calculations.
The Delinquent field on the Account screen will have the calculated delinquent amount. The delinquent charges will have the status of Past Due. The system will also spawn any penalty and interest charges at this time if setup to do so.
Note – The Date Past Due must have a date present to be considered for past due calculations.
Batch Payment Entry Process for Capital Software Utility, Property Tax and Revenue Management Applications.
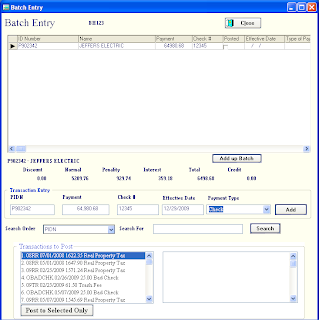
The batch payment process enables the user to quickly enter a large quantity of payments in a table style format.
1. CLICK File/Batch Payment.
2. The login screen will appear and the user name and password will have to be entered to continue with the patch payment process. (This will allow more comprehensive security entries to be made during this process.)
3. Select the Prop32 Alias from the red and white drop down menu.
4. Batch Posting box will appear that contains two rows of four buttons. You can start a new batch or add to an existing batch by CLICKING the appropriate button.
*Under the Select Type dropdown in the upper right corner, you may choose Remote Session, Normal Batch or Posted Batch. (For most postings the Normal Batch should be used. When using the Remote Payment Application select Remote Session. If an already posted batch is being accessed, choose Posted batch.)
5. The entry screen will appear and is ready for the first PIDN to be entered. From left to right the user will enter the PIDN, payment, check number and date effective (optional). Pushing the ENTER button will advance you through the fields.
If you need to search for an account, type in the Search For box and click the Search Button, find the account and double CLICK on the desired account.
When you have completed the batch, CLICK the ADD up Batch button to total the columns. If it is correct, CLICK CLOSE and continue to Step 6.
6. CLICK the POST button. Select the BATCH NUMBER (BH?) and Post the transactions. A report will launch to display the results of the Posting. Enter the BH? number to run the report.
You have entered a batch. You may edit and print reports for existing batches as often as desired.
Choosing an effective date in the batch will post the transaction as if it is that day.
Note: At the bottom of the screen there is a section marked Transactions to Post. This new addition to the batch function will allow the payment of a particular account that might have more than one charge line needing payment, to place the payment on a desired charge line. Keep in mind that the default setting is to place the payment on the oldest charge line then work down to the newest. This function will allow a user to place the payment on the desired charge line bypassing the default settings.
Defining a Tran Code within Capital Software Property Tax Software.
What is a tran code?
A transaction code (rate code) is an item setup each year by the user to accurately calculate and track all of the charges to be applied within the system. The transaction code or tran code as referred to from this point on, is the cornerstone to all calculations performed by the system.
Tran codes are typically setup for Taxes, Penalty, Interest and any miscellaneous charge such as advertising or attorney fees. You can setup a tran code for any type of tax related charge.
A tran code contains descriptions, rates, general ledger numbers, discount days and rates, penalty days and rates, interest days and rates. Each of these items must be addressed during tran code setup to guarantee the desired outcome and performance.
A transaction code (rate code) is an item setup each year by the user to accurately calculate and track all of the charges to be applied within the system. The transaction code or tran code as referred to from this point on, is the cornerstone to all calculations performed by the system.
Tran codes are typically setup for Taxes, Penalty, Interest and any miscellaneous charge such as advertising or attorney fees. You can setup a tran code for any type of tax related charge.
A tran code contains descriptions, rates, general ledger numbers, discount days and rates, penalty days and rates, interest days and rates. Each of these items must be addressed during tran code setup to guarantee the desired outcome and performance.
Information needed before setting up a Tran Code within the Capital Software Property Tax Software.
Preparation is the key to a smooth tran code setup process. Before setting up your tran codes, list out the following information on paper:
1. All possible charges that normally appear on your tax bill.
2. Assign a name to each code using a format similar to Year/type like 09RP.
3. Write down the tax rate and any multiplying factors such as per 100 or per 1000.
4. Write down any specific calculation needs for your area. For example it is common in many areas to only use a portion like 20% on the actual property assessment.
5. Write down you discount rate (negative number) if applicable
6. Write down your penalty rate .10 = 10%
7. Write down your ANNUAL interest rate (1% / month = .12% / year)
8. Write down the General Ledger account numbers for the Cash, Accounts Receivable and Revenue accounts. Ask your accountant if you do not know those numbers.
9. Write down what accounts get this charge. For example is it applied to everyone or just residential property. That will help your SQL statement.
1. All possible charges that normally appear on your tax bill.
2. Assign a name to each code using a format similar to Year/type like 09RP.
3. Write down the tax rate and any multiplying factors such as per 100 or per 1000.
4. Write down any specific calculation needs for your area. For example it is common in many areas to only use a portion like 20% on the actual property assessment.
5. Write down you discount rate (negative number) if applicable
6. Write down your penalty rate .10 = 10%
7. Write down your ANNUAL interest rate (1% / month = .12% / year)
8. Write down the General Ledger account numbers for the Cash, Accounts Receivable and Revenue accounts. Ask your accountant if you do not know those numbers.
9. Write down what accounts get this charge. For example is it applied to everyone or just residential property. That will help your SQL statement.
Capital Softwares Maintenance Program. What does it really do?
The maintenance program is a very powerful support tool. The maintenance can perform many functions. Understanding what the program does may help you understand how the program runs. The maintenance program can be configured to correct damaged tables. It can be configured to archive history. It can even be configured to correct fields that may otherwise cause a conflict in the system.
But the biggest thing that it does is re-index the tables every day. The term re-indexing means that there are fields inside of the system that is more important than others. There are fields that link all the tables together, or the fields that you search by. It indexes those fields to be able to perform those functions. If you ever encounter an error that states that the TAG is not found, then chances are the indexes need to be re-indexed to be able to perform properly. This is a very rare occurrence, but it may happen if the maintenance has not been run for a very long time.
Keep in mind that the maintenance can not be run while the system is being used for anything else. If you leave your program open when you leave for the day, it may cause another error. So make sure that you close your program every day before you leave. One other thing that you may want to check is that the backup system is not overlapping the maintenance program. This may cause a much larger problem because they are both trying to access the same files at the same time. We call that exclusive use of a table. The maintenance has to have exclusive use of all the tables to be able to perform its functions.
But the biggest thing that it does is re-index the tables every day. The term re-indexing means that there are fields inside of the system that is more important than others. There are fields that link all the tables together, or the fields that you search by. It indexes those fields to be able to perform those functions. If you ever encounter an error that states that the TAG is not found, then chances are the indexes need to be re-indexed to be able to perform properly. This is a very rare occurrence, but it may happen if the maintenance has not been run for a very long time.
Keep in mind that the maintenance can not be run while the system is being used for anything else. If you leave your program open when you leave for the day, it may cause another error. So make sure that you close your program every day before you leave. One other thing that you may want to check is that the backup system is not overlapping the maintenance program. This may cause a much larger problem because they are both trying to access the same files at the same time. We call that exclusive use of a table. The maintenance has to have exclusive use of all the tables to be able to perform its functions.
Monday, December 28, 2009
Multiple Payment Reversal Instructions for Captial Software Utility, Property Tax and Revenue Management Softwares.
Multiple Payment Reversal
1. Locate the first account of the multiple payment that needs the payment reversed.
2. On the Payment screen, push the Reverse Payment button.
The reversal screen will be displayed.
3. Select a reason for the reversal and any notes pertaining to this reversal for a good audit trail.
4. If you DO want this reversal to show up on TODAY’s balancing reports leave the check mark (This would be for a reversal performed the same day the payment is taken).
If you DO NOT want this reversal to show up on balancing reports REMOVE the check mark.
5. In the section that displays the line items, highlight ONLY THE MULTIPLE line item. Once the transactions are highlighted, push the REVERSE SELECTED button. Wait until the process is finished.
6. Then exit out of the reverse screen and you will find a new entry on your payments tab. The reverse function will also make the proper gl entries and put the charge back on the Charges screen.
Go to the next account that was part of the multiple payment and repeat steps 2 thru 6.
Note – The entry made for Balancing Reversals has a type of REVPAY. The entry made for a non balancing reversal is XREVPAY. Gl entries are always made but the type determines whether it shows up on the daily balancing reports.
1. Locate the first account of the multiple payment that needs the payment reversed.
2. On the Payment screen, push the Reverse Payment button.
The reversal screen will be displayed.
3. Select a reason for the reversal and any notes pertaining to this reversal for a good audit trail.
4. If you DO want this reversal to show up on TODAY’s balancing reports leave the check mark (This would be for a reversal performed the same day the payment is taken).
If you DO NOT want this reversal to show up on balancing reports REMOVE the check mark.
5. In the section that displays the line items, highlight ONLY THE MULTIPLE line item. Once the transactions are highlighted, push the REVERSE SELECTED button. Wait until the process is finished.
6. Then exit out of the reverse screen and you will find a new entry on your payments tab. The reverse function will also make the proper gl entries and put the charge back on the Charges screen.
Go to the next account that was part of the multiple payment and repeat steps 2 thru 6.
Note – The entry made for Balancing Reversals has a type of REVPAY. The entry made for a non balancing reversal is XREVPAY. Gl entries are always made but the type determines whether it shows up on the daily balancing reports.
Payment Reversal Instructions for Capital Software Utility, Property Tax and Revenue Management Softwares.
1. Locate the account that needs the payment reversed.
2. On the Payment screen, push the Reverse Payment button.
The screen above will be displayed.
The screen above will be displayed.
3. Select a reason for the reversal and any notes pertaining to this reversal for a good audit trail.
If you DO want this reversal to show up on TODAY’s balancing reports leave the check mark (This would be for a reversal performed the same day the payment is taken).
If you DO NOT want this reversal to show up on balancing reports REMOVE the check mark.
If you DO want this reversal to show up on TODAY’s balancing reports leave the check mark (This would be for a reversal performed the same day the payment is taken).
If you DO NOT want this reversal to show up on balancing reports REMOVE the check mark.
4. In the section that displays the line items, highlight only the payment line item that is part of the transaction. Once the transactions are highlighted, push the REVERSE SELECTED button. Wait until the process is finished.
5. Then exit out of the reverse screen and you will find a new entry on your payments tab. The reverse function will also make the proper gl entries and put the charge back on the Charges screen.
Note – The entry made for Balancing Reversals has a type of REVPAY. The entry made for a non balancing reversal is XREVPAY. Gl entries are always made but the type determines whether it shows up on the daily balancing reports.
Single Payment Reversal Instructions for Capital Software Utility, Property Tax and Revenue Management Softwares.
1. Locate the account that needs the payment reversed.
2. On the Payment screen, push the Reverse Payment button.
The screen above will be displayed.
3. Select a reason for the reversal and any notes pertaining to this reversal for a good audit trail.
If you DO want this reversal to show up on TODAY’s balancing reports leave the check mark (This would be for a reversal performed the same day the payment is taken).
If you DO NOT want this reversal to show up on balancing reports REMOVE the check mark.
4. In the section that displays the line items, highlight only the payment line item that is part of the transaction. Once the transactions are highlighted, push the REVERSE SELECTED button. Wait until the process is finished. Then exit out of the reverse screen and you will find a new entry on your payments tab. The reverse function will also make the proper gl entries and put the charge back on the Charges screen.
Note – The entry made for Balancing Reversals has a type of REVPAY. The entry made for a non balancing reversal is XREVPAY. Gl entries are always made but the type determines whether it shows up on the daily balancing reports.
2. On the Payment screen, push the Reverse Payment button.
The screen above will be displayed.
3. Select a reason for the reversal and any notes pertaining to this reversal for a good audit trail.
If you DO want this reversal to show up on TODAY’s balancing reports leave the check mark (This would be for a reversal performed the same day the payment is taken).
If you DO NOT want this reversal to show up on balancing reports REMOVE the check mark.
4. In the section that displays the line items, highlight only the payment line item that is part of the transaction. Once the transactions are highlighted, push the REVERSE SELECTED button. Wait until the process is finished. Then exit out of the reverse screen and you will find a new entry on your payments tab. The reverse function will also make the proper gl entries and put the charge back on the Charges screen.
Note – The entry made for Balancing Reversals has a type of REVPAY. The entry made for a non balancing reversal is XREVPAY. Gl entries are always made but the type determines whether it shows up on the daily balancing reports.
Sunday, December 20, 2009
Capital Launches New Interactive Tools
Capital tech support is starting 2010 in a big way. With the launch of Capital's new website you can now
Launch a remote desktop session
Enter and review support tickets online
Research tech topics on the blog
And much more.
Check out the new site at www.capitalsoftwareinc.com
Sent from my Verizon Wireless BlackBerry
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)